Customer Stories
Ballast Nedam Milieu Techniek, https://www.ballast-nedam.nl/
We experience Spirofil as a company with fast service, available 24 hours a day. They have been our supplier for 25 years. We have always had a pleasant relationship with their staff!
Aquafin NV , https://www.aquafin.be/
During the past period, we have had a consistent and reliable partner, which is essential for our operational activities. Spirofil’s commitment to quality and timely deliveries has helped us ensure smooth production processes and keep our teams satisfied.
Attero, https://www.attero.nl
Attero has been doing business with Spirofil for years based on trust and their quick response time, combined with the quality of the work performed. Personally, I hope to continue doing business with them for many more years to come.
Hoogheemraadschap van Rijnland, https://www.rijnland.net/
…
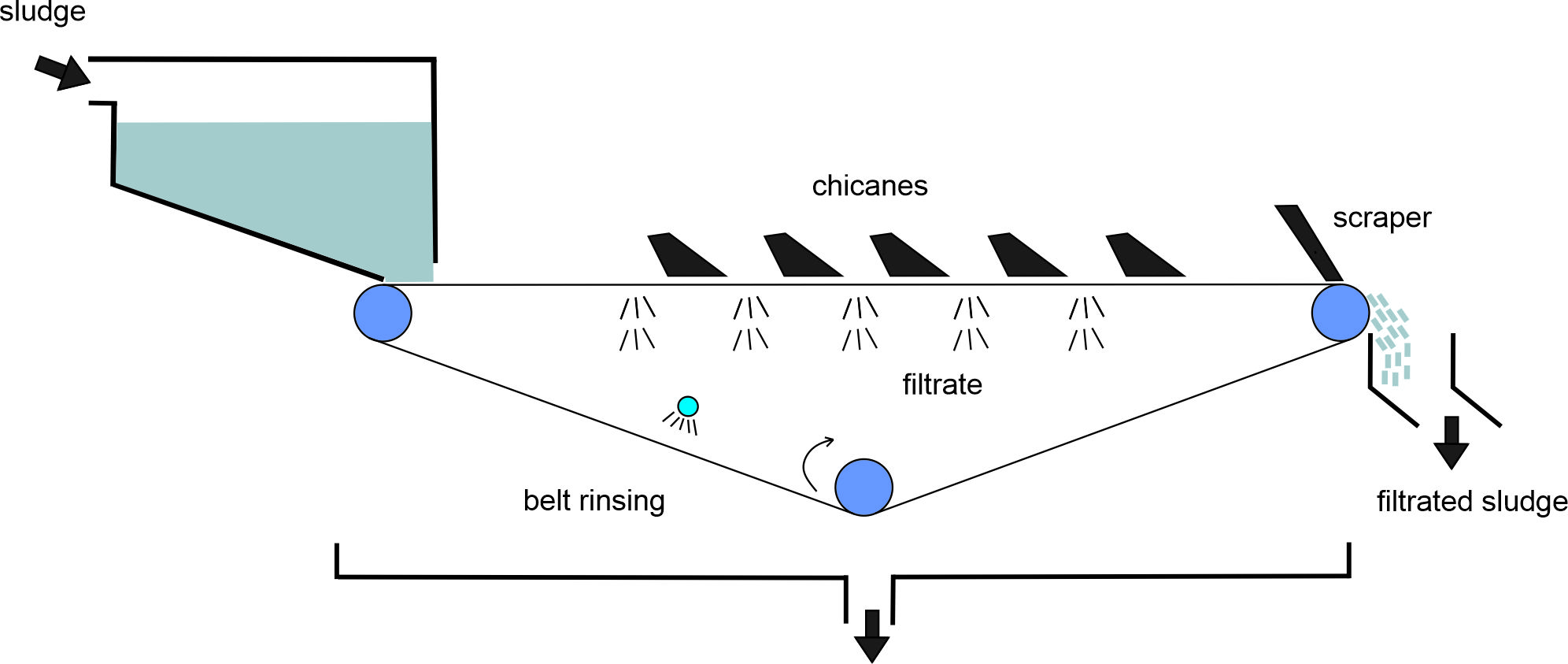
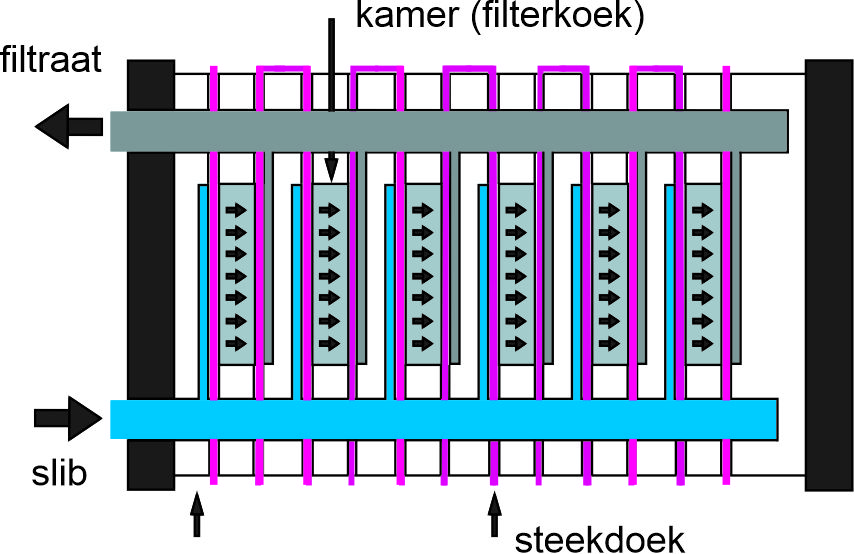
Spirofil maintains, renovates, and optimizes dewatering installations

Spirofil B.V.
Fluorietweg 23 B
NL-1812 RR Alkmaar
The Netherlands
Phone +31 (0)72 2035050
Email info@spirofil.eu
Company
Copyright Spirofil B.V.
Created by BRNDXP | Privacy Policy